Electric Reactor
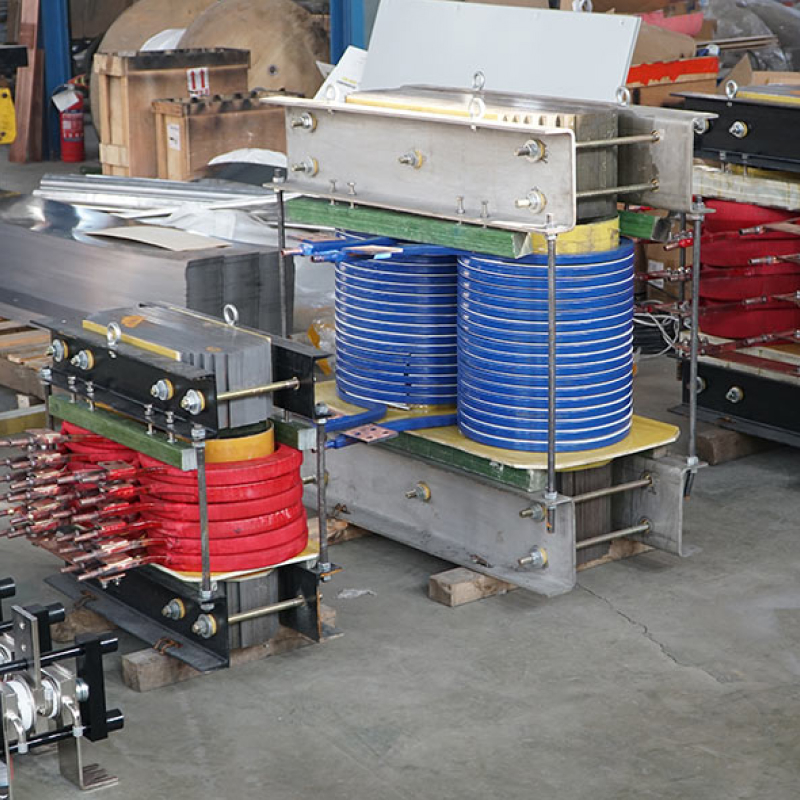
An electric reactor, also known as a reactor coil or simply reactor, is an electrical component used in power systems for the purpose of controlling and stabilizing voltage, current, and power flow. It is a passive device that consists of a coil of wire wound around a core material, typically made of iron or other magnetic materials.
Features of Electric Reactors:
-
Inductance: Electric reactors exhibit inductance due to the coil of wire wound around the core material. This inductance opposes changes in current flowing through the reactor, thereby helping to stabilize the electrical system.
-
Control of Current and Voltage: By varying the number of turns in the coil or adjusting the magnetic properties of the core material, electric reactors can be designed to control current and voltage levels in the electrical system. They can limit the rate of change of current (di/dt) and voltage (dv/dt), reducing stress on other components and improving system stability.
-
Filtering and Harmonic Suppression: Electric reactors can be used in conjunction with capacitors to form LC (inductor-capacitor) filters, which are commonly employed to suppress harmonics and filter out undesirable frequencies from the power system. This helps to improve power quality and prevent equipment damage.
-
Fault Current Limiting: In electrical systems, electric reactors can act as fault current limiters by limiting the magnitude of fault currents during short-circuit conditions. This protects equipment and reduces the risk of damage to the electrical system.
-
Voltage Regulation: Electric reactors can help regulate voltage levels in the electrical system by absorbing or supplying reactive power as needed. They can compensate for voltage fluctuations caused by changes in load or supply conditions, ensuring stable voltage levels at various points in the system.
Why trust?
- INTRODUCTION
An electric reactor, also known as a reactor coil or reactor, is an electrical component used in power systems for controlling and stabilizing voltage, current, and power flow. It is a passive device that consists of a coil of wire wound around a core material, typically made of iron or other magnetic materials.
Application
The applications of HK Frequency’s products span across a diverse range of industries and sectors, where precision frequency control and reliable power electronics are essential for various operations. Some of the key applications include:
Voltage Regulation: Electric reactors are used in power systems to regulate voltage levels, particularly in distribution networks where fluctuations in load demand can lead to voltage variations. By adjusting the inductance of the reactor, voltage levels can be stabilized and maintained within acceptable limits.
Harmonic Filtering: In systems with non-linear loads such as power electronics converters and variable frequency drives, electric reactors are employed to suppress harmonics and filter out undesirable frequencies. This helps improve power quality and prevent equipment damage caused by harmonic distortion.
Fault Current Limiting: During short-circuit conditions, electric reactors can limit the magnitude of fault currents, thereby protecting equipment and minimizing damage to the electrical system. They act as current-limiting devices, reducing stress on other components and improving overall system reliability.
Motor Starting and Control: Electric reactors are used in motor control applications to limit the inrush current during motor starting, preventing damage to the motor windings and associated circuitry. They also provide smooth and gradual acceleration, enhancing motor control and efficiency.